Early Treatment of a Brain Hematoma Can Save Lives
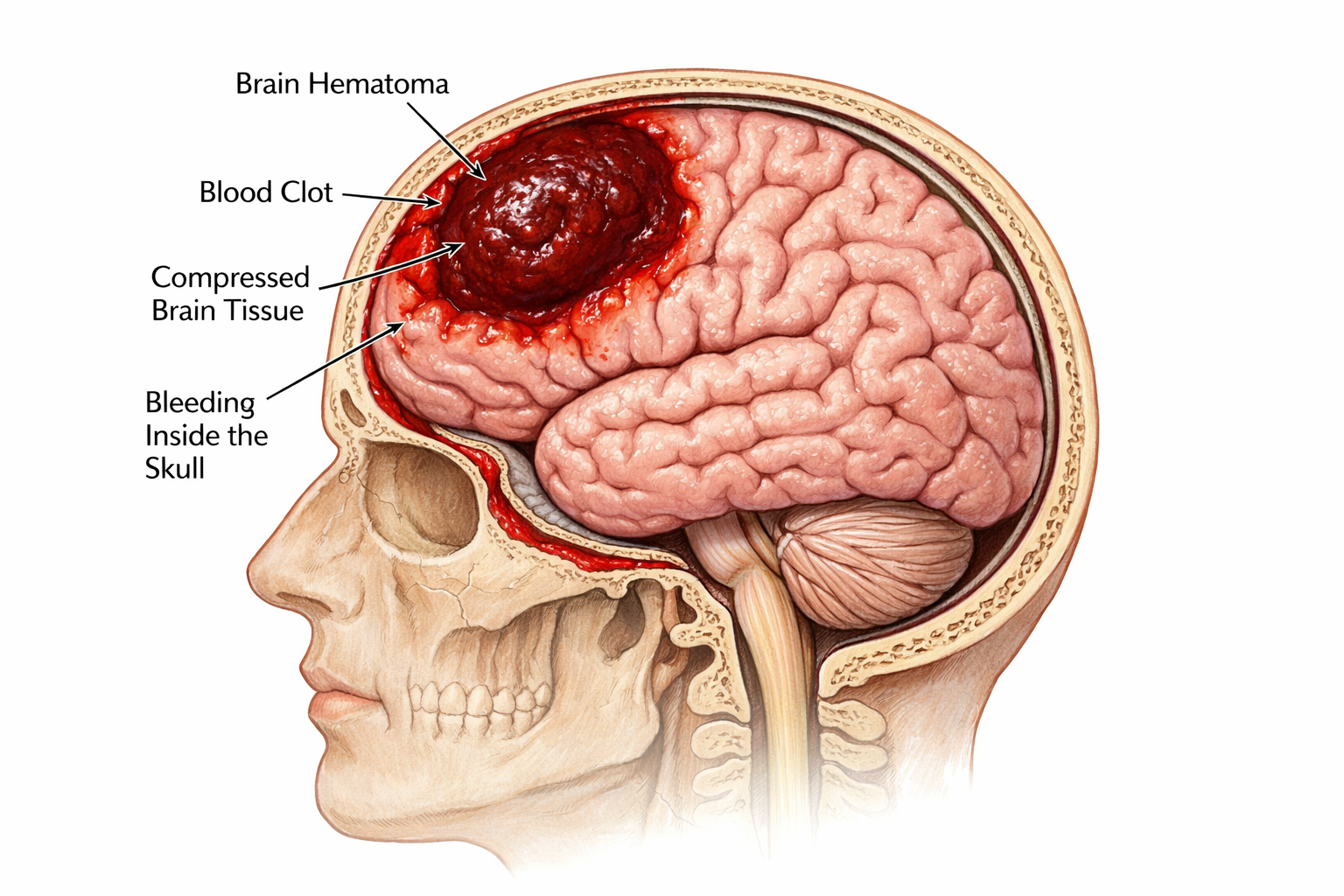
Many people are not aware that even a small amount of bleeding inside the brain can become life-threatening if ignored. A brain hematoma is a condition where blood collects inside or around the brain, usually after a fall, road accident, head injury, or trauma. In some elderly patients, it can occur even after a minor injury.
Initially, symptoms like headache, dizziness, nausea, or sleepiness may appear mild. Because of this, warning signs are often ignored. However, the brain is extremely sensitive, and increasing pressure inside the skull can cause serious damage within a short time.
The positive aspect is that early diagnosis and timely treatment of brain hematoma can save lives and prevent permanent brain damage. With prompt medical care, many patients recover well and return to normal daily life.
What Is a Brain Hematoma?
A brain hematoma occurs when blood accumulates inside the skull. Since the skull is rigid and cannot expand, this collected blood increases pressure on the brain. This pressure can affect vital brain functions such as movement, speech, memory, and even breathing.
Common Causes of Brain Hematoma
-
Head injury or trauma
-
Road traffic accidents
-
Falls, especially in elderly individuals
-
Sports-related injuries
-
Long-term use of blood-thinning medications
Symptoms of Brain Hematoma
-
Severe or persistent headache
-
Vomiting or nausea
-
Confusion or drowsiness
-
Weakness on one side of the body
-
Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
-
Seizures
-
Loss of consciousness
Symptoms may appear immediately after injury or develop slowly over days or weeks. This is why even a minor head injury should never be ignored. CT scans and MRI scans help detect brain hematomas early and guide treatment decisions.
Urgent Treatment Options for Brain Hematoma
A brain hematoma is a medical emergency and requires immediate medical attention. The primary goal of treatment is to reduce pressure on the brain and prevent further damage.
Medical Management
If the bleeding is small and the patient is stable:
-
Medications are given to reduce brain swelling
-
Blood pressure is carefully controlled
-
Anti-seizure medicines may be prescribed
-
Continuous monitoring in the hospital or ICU
Surgical Treatment
If the bleeding is large or the patient’s condition is worsening:
-
Emergency surgery may be required
-
Surgery removes the collected blood and relieves pressure on the brain
Early surgical intervention can be life-saving and significantly improve recovery. Delay in treatment can result in permanent brain injury or death.
Whom to Consult for Brain Hematoma Treatment
If a brain hematoma is suspected, the patient should be taken immediately to a hospital with emergency and imaging facilities.
The condition is treated by a neurosurgeon, a specialist trained in brain and spine disorders. After clinical evaluation and brain imaging, the neurosurgeon decides whether medical management or surgery is required.
Dr. Aditya Gupta, a highly experienced brain and spine specialist, provides advanced treatment for brain hematomas using evidence-based medical care and modern neurosurgical techniques.
Choosing a hospital with 24/7 CT/MRI scans, ICU support, and neurosurgery services is critical for the best outcome.
Recovery Time After a Brain Hematoma
Recovery time varies from patient to patient and depends on:
-
Size and location of the hematoma
-
Patient’s age and overall health
-
Severity of symptoms
-
How early treatment was started
Expectations:
-
Mild cases treated early may recover within a few weeks
-
Severe cases or post-surgery recovery may take several months
During recovery, patients may feel tired, weak, or experience slowed thinking. These symptoms usually improve with time, rest, rehabilitation, and regular follow-ups. Physiotherapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy can help speed up recovery.
Surgery vs Medical Management: Which Is Needed?
Not every brain hematoma requires surgery. The treatment approach depends on the patient’s condition and scan findings.
When Medical Treatment Is Enough
-
Small and stable hematomas
-
No worsening neurological symptoms
-
Close monitoring with repeat brain scans
When Surgery Is Required
-
Large hematomas causing brain pressure
-
Worsening symptoms or reduced consciousness
-
Shift of brain structures seen on scans
Doctors always choose the safest and most effective treatment plan to protect brain function and save life.
When Can the Patient Go Home?
A patient can be discharged when:
-
Vital signs are stable
-
Neurological symptoms are improving
-
Brain scans show no danger signs
Some patients may go home within a few days, while others—especially after surgery—may require a longer hospital stay. Recovery continues at home with medications, rest, activity restrictions, and follow-up care.
Follow-Up Care and Instructions
Regular follow-up is essential for complete recovery:
-
Attend all scheduled follow-up visits
-
Repeat brain scans if advised
-
Continue medications as prescribed
-
Immediately report symptoms like headache, vomiting, seizures, or confusion
Early treatment, regular monitoring, and a positive recovery approach lead to the best long-term outcomes in patients with brain hematoma.
- Tags:
- best neurosurgeon for brain hematoma
- bleeding in brain treatment
- brain bleed emergency treatment
- brain hematoma diagnosis and treatment
- brain hematoma surgery
- brain hematoma treatment
- brain hemorrhage vs hematoma
- brain pressure relief surgery
- CT scan brain hematoma
- elderly brain hematoma treatment
- emergency neurosurgery India
- head injury brain bleeding
- ICU care for brain bleeding
- intracranial hematoma surgery
- MRI brain bleeding
- neurosurgeon for brain hematoma
- neurosurgery for brain bleed
- recovery after brain hematoma surgery
- subdural hematoma treatment
- traumatic brain injury bleeding