What is Epilepsy?
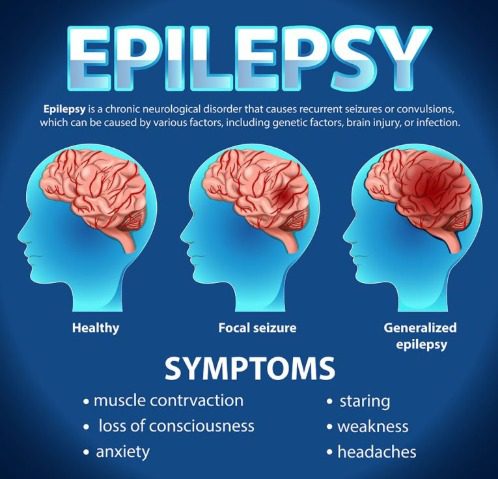
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures resulting from abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It affects individuals of all ages and backgrounds, with varying degrees of severity and manifestation. Understanding epilepsy involves exploring its types, causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options.

Types of Epilepsy
- Epilepsy is broadly categorized based on the origin and nature of seizures:
- Generalized Epilepsy: Seizures involve the entire brain from the onset. Common types include:
- Absence Seizures: Characterized by brief, sudden lapses in consciousness, often mistaken for daydreaming.
- Tonic-Clonic Seizures: Involve a combination of muscle stiffening (tonic phase) and rhythmic jerking movements (clonic phase), typically lasting a few minutes.
- Focal Epilepsy: Seizures originate in a specific area of the brain and may present as:
- Focal Aware Seizures: The person remains conscious and may experience unusual sensations or movements.
- Focal Impaired Awareness Seizures: Involves altered consciousness, often accompanied by repetitive movements.
- Unknown Epilepsy: When the onset of seizures is unclear or cannot be determined.
Causes of Epilepsy
- The etiology of epilepsy is diverse and can be attributed to various factors:
- Genetic Factors: Certain types of epilepsy run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Brain Injuries: Traumatic brain injuries from accidents or falls can lead to epilepsy.
- Neurological Diseases: Conditions like stroke or brain tumors may trigger epileptic seizures.
- Infections: Central nervous system infections such as meningitis or encephalitis can cause epilepsy.
- Prenatal Injuries: Brain damage occurring before birth due to factors like oxygen deprivation or maternal infections can result in epilepsy.

Symptoms of Epilepsy
- The manifestations of epilepsy vary depending on the type of seizure:
- Seizures: The hallmark of epilepsy, seizures can range from brief lapses in attention to severe convulsions.
- Temporary Confusion: Especially common after a seizure, known as the postictal state.
- Staring Spells: Particularly in absence seizures, where the individual appears to be staring blankly.
- Uncontrollable Jerking Movements: Typically involving the arms and legs.
- Loss of Consciousness or Awareness: Occurs in certain types of seizures.
Why is Epilepsy Surgery Needed?
Epilepsy surgery is considered when seizures cannot be effectively controlled with medication. For many patients, surgery offers a chance to significantly reduce or even eliminate seizures, improving their overall quality of life. Below are the key reasons why epilepsy surgery may be necessary:
- Medications Are Ineffective
Anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) are the first line of treatment for epilepsy. However, in some cases, medications fail to control seizures effectively. This condition, known as drug-resistant epilepsy, affects a significant number of patients, making surgery a viable option. Additionally, some individuals experience severe side effects from medications, such as drowsiness, mood changes, or organ damage, which may impact daily life. When medication alone is not sufficient, surgery can help target and remove the area of the brain responsible for seizures, offering a better long-term solution. - Improving Quality of Life
Frequent seizures can interfere with daily activities, making it difficult for individuals to work, drive, or engage in social activities. Epilepsy can also lead to emotional distress, increasing the risk of anxiety and depression due to the unpredictability of seizures. Surgery can significantly reduce or eliminate seizures, allowing patients to regain independence, improve their mental well-being, and lead a more fulfilling life. Additionally, managing epilepsy with surgery can reduce long-term medical expenses associated with hospital visits, medications, and emergency care, lowering the overall cost of living with the condition.
For patients who qualify, epilepsy surgery can be life-changing, offering a chance to gain better seizure control, reduce dependence on medication, and restore confidence in daily activities.
More than ninety percent of epilepsy patients require medical treatment alone. Sometimes, when more than three medicines in maximum doses are not able to take care of epilepsy, we need to evaluate the patient for epilepsy surgery. This evaluation includes a special epilepsy protocol MRI and a video EEG. This testing and evaluation is typically done by an epilepsy expert neurologist.
Diagnosis of Epilepsy
- Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and involves:
- Medical History: Detailed account of seizure occurrences, family history, and any underlying conditions.
- Neurological Examination: Assessment of motor abilities, sensory function, and cognitive skills.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): Records electrical activity in the brain to detect abnormalities.
- Imaging Studies: MRI or CT scans to identify structural abnormalities or lesions in the brain.
Treatment Options for Epilepsy
- Management of epilepsy is tailored to the individual’s needs and may include:
- Medications: Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are the primary treatment, effectively controlling seizures in many patients.
- Surgery: Considered when seizures are resistant to medication and originate from a specific brain area.
- Therapies: Options like vagus nerve stimulation or responsive neurostimulation may be utilized.
- Dietary Approaches: Ketogenic or modified Atkins diets have been beneficial in some cases.
Patient Stories
Can epilepsy be cured?
Epilepsy is a neurological condition that can often be controlled with medication or surgery, but not all types are curable. Some individuals may become seizure-free over time, while others may require long-term management. Advances in treatment have significantly improved outcomes for many patients.
Are epilepsy and seizures the same thing?
No, epilepsy and seizures are not the same. A seizure is a sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbance in the brain. Epilepsy is a medical condition where a person has a tendency to experience recurrent seizures.
What causes epilepsy?
Epilepsy can result from various factors such as head injuries, brain infections, stroke, genetic conditions, or developmental disorders. In many cases, the exact cause remains unknown despite thorough evaluation.
What is epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures. It affects people of all ages and can vary in severity, frequency, and type of seizure experienced.
When does epilepsy typically occur?
Epilepsy can begin at any age, but it most commonly starts in childhood or after the age of 60. The timing often depends on the underlying cause, such as genetic factors or brain injury.




